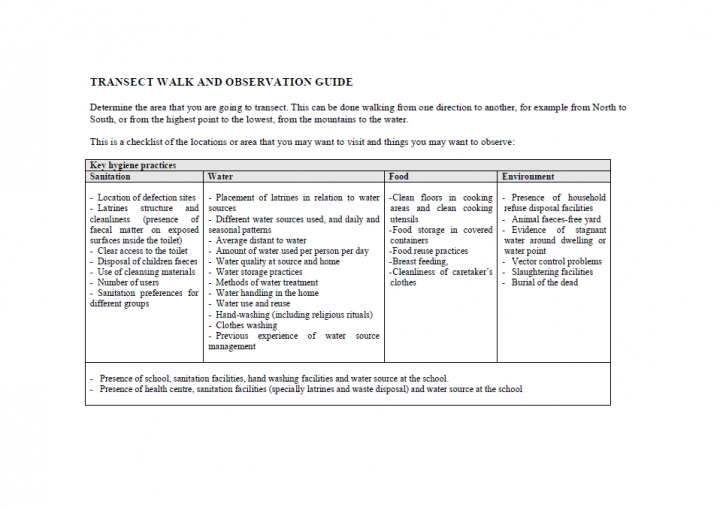
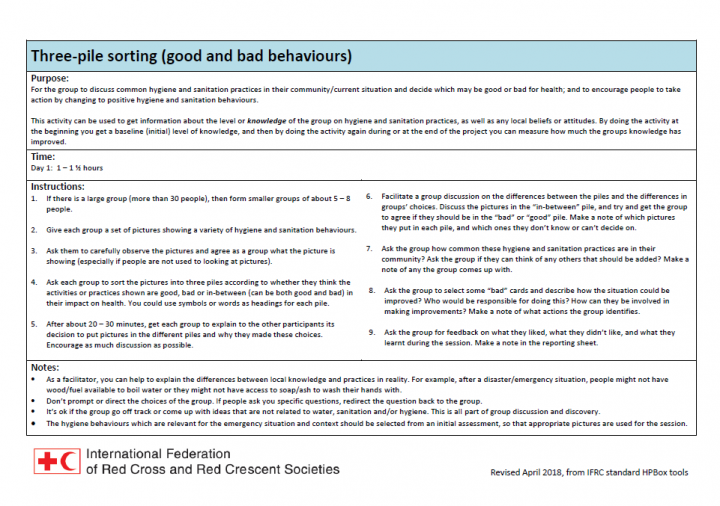
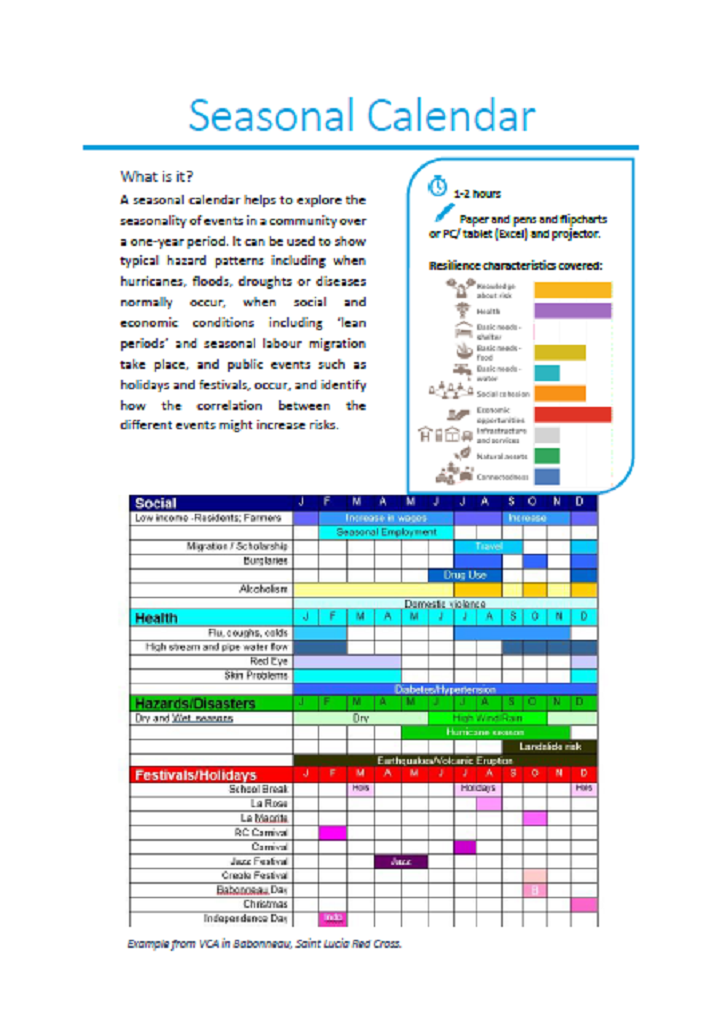
IFRC (0) Transect Walk. EVCA Toolbox
A transect walk involves walking through the community to observe and discuss the daily activities, the surroundings and the risks and resources. It is used to note the sites and topography of the area, to understand interrelationships based on space. It is a useful exercise to do in the assessment stage to get a feeling for the issues and capacities which exist in a community. […]
Oxfam (2018) An Introduction to Community Engagement in WASH
The overall aim of Oxfam’s WASH response in emergencies is to minimise public health risks in relation to water, sanitation and hygiene. This means working more directly with a wide range of people affected by the crisis to better understand them, to motivate them to make positive behaviour changes, and to strengthen their capacity to reduce/prevent public health risks and make their own decisions. We […]
Oxfam (0) Working with Children in Humanitarian WASH Programmes
Children under five years can represent up to 20% of the population. In some cases children under 18 years may represent over 50% of the population. They are thus major stakeholders in all humanitarian programmes. This briefing paper describes the practical issues that need to be considered when involving children in humanitarian WASH programmes.
Otieno, P. V. (2012) The 'Shame Question' in CLTS.
There has been an interesting debate going on about the elements of shame, fear and disgust used during CLTS triggering session. The debate has been between those who believe that the element of shame as applied during a CLTS trigger is unethical as it amounts to degrading and embarrassing the community, and those who believe that the element of shame is actually positive, and that […]
IFRC (2020) Protection, Gender and Inclusion in Water, Sanitation and Hygiene. Guidance Note
This guidance note provides an overview of key PGI issues to consider when assessing, designing, implementing and monitoring both long-term and humanitarian WASH programmes, in the Red Cross Red Crescent context.
IFRC (2019) Menstrual Hygiene Management Guideline and Tools
Menstrual hygiene management, or MHM, refers to a range of actions and interventions that ensure that people who menstruate can privately, safely and hygienically manage their menstruation with confidence and dignity. MHM is not only about distributing pads or providing education to girls. Effective MHM actions have three main components: i) MHM materials and supportive items, ii) Private, safe and appropriate WASH facilities, and iii) […]
IFRC (2005) Guidelines for Emergency Assessment
1.1 Why is an assessment methodology necessary? Assessment is a vital element of the programme-planning process. Assessment provides the information on which decisions will be made. Whilst good information does not guarantee a good programme, poor information almost certainly guarantees a bad one. The use of a standard methodology means that information can be compared with data collected during previous assessments. 2.2 Who will use these guidelines? The […]
Oxfam (2007) The Good Enough Guide. Impact Measurement and Accountability in Emergencies. Emergency Capacity Building Project.
What difference are we making? How do we know? The Good Enough Guide helps busy field workers to address these questions. It offers a set of basic guidelines on how to be accountable to local people and measure programme impact in emergency situations. Its 'good enough' approach emphasises simple and practical solutions and encourages the user to choose tools that are safe, quick, and easy to […]
IFRC (0) Focus Group Discussion Guide – Assessment. Menstrual Hygiene Management in Emergencies
These guidelines outline a step-by-step process for Red Cross Red Crescent staff and volunteers to plan and implement effective, context appropriate hygiene promotion, without taking shortcuts or delivering ‘hygiene messages’. The guidelines provide National Societies with a standard approach for quality assurance, and an opportunity for more effective training and monitoring.
OHCHR (0) Checklist for Mainstreaming Protection in WASH Programmes. Protection and WASH Cluster.
This checklist is a tool to assist in incorporating protection in water and sanitation interventions. The questions are intended to assist organizations in identifying issues that should be factored into the design, implementation, monitoring and evaluation of their programmes and projects.
Nzioki, M.N., Korir, A (2020) Effective Methods for Community Sanitation and Hygiene Promotion in the Developing World: A Scoping Review
World Health Organization data on the burden of disease shows that approximately 3.1% of deaths (1.7 million) and 3.7% (54.2 million) of disability-adjusted-life-years (DALYs) worldwide are attributable to unsafe water, sanitation and hygiene. In Africa and developing countries in South East Asia 4-8% of all disease burdens are attributable to poor hygiene and sanitation. Over 99.8% of all deaths in developing world are attributable to […]
IFRC (2020) Feedback Starter Kit. Tool 15
This feedback starter-kit responds to key questions and provides the most important tips for setting up and running a simple feedback mechanism. The kit includes an overview of templates containing the necessary basic elements to implement and run a feedback mechanism. All tools can be found under the 'related resources' section of this page.
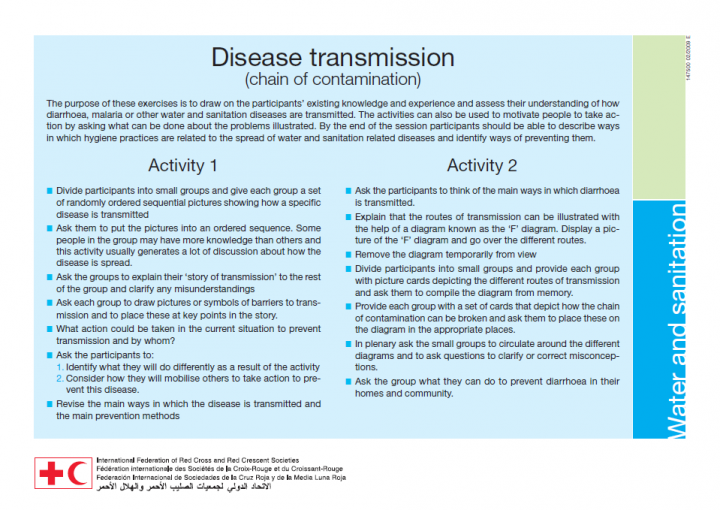
IFRC (2009) Disease Transmission (Chain of Contamination)
The purpose of these exercises is to draw on the participants’ existing knowledge and experience and assess their understanding of how diarrhoea, malaria or other water and sanitation diseases are transmitted. The activities can also be used to motivate people to take action by asking what can be done about the problems illustrated. By the end of the session participants should be able to describe […]