González P., M. E. (2014) Sanitising faecal sludge with ammonia (from urea) in the context of emergency situations Master thesis
In an emergency situation, the collection, treatment and disposal of the human excreta and waste in a safe way is one of the biggest challenges to face, regardless the type of disaster. When it comes to faecal sludge management, the traditional desludging methods can often not be appropriate in an acute emergency phase. Consequently, relief organisations aim to apply new and simple approaches and modular […]
Nordin, A., Nyberg, K., Vinneras, B. (2009) Inactivation of Ascaris Eggs in Source-Separated Urine and Feces by Ammonia at Ambient Temperatures
Sustainable management of toilet waste must prevent disease transmission but allow reuse of plant nutrients. Inactivation of uterus-derived Ascaris suum eggs was studied in relation to ammonia in source-separated urine without additives and in human feces to which urea had been added, in order to evaluate ammonia-based sanitation for production of safe fertilizers from human excreta. Urine was used concentrated or diluted 1:1 and 1:3 […]
USAID (2015) Implementer’s Guide to Lime Stabilisation for Septage Management in the Philippines
Local government units (LGUs) just beginning to implement a new septage management program may wish to phase in the program over time. Lime stabilization can be done as a first phase following a disaster and perhaps serve the public and commercial sectors. In the next phase, a municipal or city-wide program to desludge all septic tanks on a regular schedule using treatment technologies besides lime […]
Sozzi, E., Fesselet, J. F., Taylor, H. (2011) Standard operating procedure for the physicochemical treatment of CTC wastewaters
When cholera strikes in a low-income country, the rapid construction and successful operation of specialist cholera treatment centres (CTC) by medical NGOs can significantly reduce the mortality rate. Such has been the case in Haiti. Since cholera struck the eastern part of the island of Hispaniola in October 2010, in the aftermath of a devastating earthquake ten months earlier, Médecins Sans Frontières has operated five […]
Chakraborty I., Capito, M., Jacks, C., Pringle R. (2014) Household-level application of hydrated lime for on-site treatment and agricultural use of latrine sludge
Rural areas of Cambodia have no safe waste management strategies for household latrine waste. Household application of lime (calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2) would enable households to treat waste easily on-site and significantly reduce the risk of latrine sludge causing negative impacts on human health and the environment, whilst transforming latrines into incubators of a valuable agricultural additive. Initial investigative work – including human centered design research, […]
Anderson, C., Malambo, D. H., Perez, M. E., Nobela, H. N., de Pooter, L., Spit, J., Hooijmans, C. M., de Vossenberg, J. V., Greya, W., Thole, B., van Lier, J. B., Brdjanovic, D. (2015) Lactic Acid Fermentation, Urea and Lime Addition Promising Faecal Sludge Sanitizing Methods for Emergency Sanitation
In this research, three faecal sludge sanitizing methods—lactic acid fermentation, urea treatment and lime treatment—were studied for application in emergency situations. These methods were investigated by undertaking small scale field trials with pit latrine sludge in Blantyre, Malawi. Hydrated lime was able to reduce the E. coli count in the sludge to below the detectable limit within 1 h applying a pH > 11 (using […]
Mamani, G., Visser, K., Spit. J., Heeger, J., Dargere, N., Postma, S., Gijsbers, R., Mulder, R., Buyle, G. (2014) Speedkits - Rapid deployable kits as seeds for self-recovery
Within S(P)EEDKITS, workpackage WP3- “watsan” (water and sanitation) focuses on the development of flexible sanitation solutions suited for emergency cases and on low cost water kits that help to generate, transport and store (potable) water. Focus in both domains is on the easy deployment of the kits. This document reports on the prototypes for the various watsan kits and the outcome of the (first) testing.
Vögeli, Y., Lohri, C. R., Gallardo, A., Diener, S., Zurbrügg, C. (2014) Anaerobic Digestion of Biowaste in Developing Countries Practical Information and Case Studies
Research on anaerobic digestion solutions for low - and middle-income countries has shown that there is a wealth of knowledge and experience with small- and medium-scale digesters built in rural areas where manure from a few cattle and some household waste is used as feedstock. However, anaerobic digestion still seems to play a negligible role as a treatment option in urban settings for organic yard, […]
Khatavkar, A., Matthews, S. (2013) Bio-Latrines
A Bio-latrine is low maintenance system comprising a combination of a toilet and a bio-digester unit. It can be constructed using local materials and requires no machinery or fuel input other than human waste. This brief looks at the option of using bio-latrines, an on-site dry toilet technology which generates fertilising materials and fuel from the human excreta.
Rose, D. G. (1999) Community-Based Technologies for Domestic Wastewater Treatment and Reuse Options for urban agriculture
This report is the product of a five-month Centre Internship at the International Development Research Centre - Cities Feeding People Programme Initiative (CFP) during the summer of 1999. The report was commissioned to provide CFP team members an overview of emergent trends in environmentally sound and economically viable approaches to wastewater management. The subject of the report relates to the management of domestic human waste […]
Foxon, K. M., Pillay, S., Lalbahadur, T., Rodda, N., Holder, F., Buckley, C. A. (2004) The anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) An appropriate technology for on-site sanitation
This project has studied the appropriateness of the ABR for on-site primary sanitation in low-income communities. The baffled design of the ABR ensures high solids retention resulting in high treatment rates, while the overall sludge production is characteristically low. Effluent COD values measured from a 3 000 l pilot ABR using domestic wastewater at a wastewater treatment works were consistently below 200 mgCOD/l at an […]
Polprasert, C., Rajput, V. S. (1982) Septic Tank and Septic Systems Environmental Sanitation Reviews
This paper presents a state-of-the-art review on the septic tank and septic systems. Information on design and functional aspects, and environmental effects of septic tank systems are presented. In addition, some important research needs as reported in the literature are pinpointed. It should be noted that this review paper contains neither standards nor rules and regulations pertaining to septic tank and septic systems. The design […]
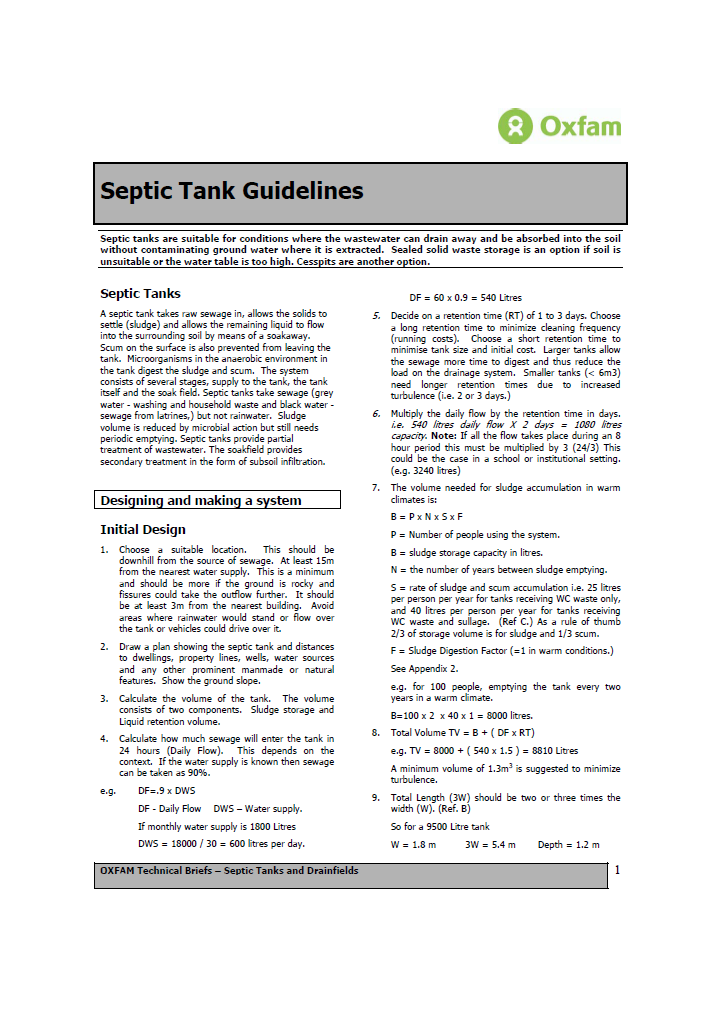
Oxfam (2008) Septic Tank Guidelines
A septic tank takes raw sewage in, allows the solids to settle (sludge) and allows the remaining liquid to flow into the surrounding soil by means of a soakaway. Scum on the surface is also prevented from leaving the tank. Microorganisms in the anaerobic environment in the tank digest the sludge and scum. The system consists of several stages, supply to the tank, the tank […]
Furlong C., Lamb, J., Bastable, A. (2017) Learning from Oxfam’s Tiger Worm Toilets projects
The world is witnessing the highest levels of forced human displacement on record, leading to people being housed in urban centres and camps. Generally the sanitation needs of these people are initially met by external agencies. The long-term costs of operating and maintaining traditional sanitation systems can be unviable when communities or local authorities take over their management. Therefore Oxfam has been trialling the Tiger […]
Furlong, C., Gibson, W. T., Oak, A., Thakar, G., Kodgire, M. (2016) Technical and user evaluation of a novel worm-based, on-site sanitation system in rural India
The technical performance and user acceptance of a novel on-site sanitation system based on vermifiltration was tested for over 12 months in rural India. Ten households (mean household size = 5.6 people) who had previously practised open defecation trialled a pour flush toilet linked to a vermifilter, together known as a ‘Tiger Toilet’. Technical parameters which were monitored over this period included: usage, temperature, accumulation […]
Furlong, C., Gibson, W. T., Templeton, M. R., Taillade, M., Kassam, F., Crabb, G., Goodsell, R., McQuilkin, J., Oak, A., Thakar, G., Kodgire, M., Patankar, R. (2015) The development of an onsite sanitation system based on vermifiltration: the `tiger toilet'
This paper describes the development of a novel onsite sanitation system based on vermifiltration, the Tiger Toilet. Initial laboratory experiments demonstrated that feed distribution was not required, a worm density of 2 kg/m2 could be used, worms preferred wetter environments, and system configuration did not affect effluent quality. Installing the first prototype in the UK proved that the process functioned when scaled, i.e. COD and […]
Thakur, P., Singh, S. (2017) SFD Report - Patna, India SFD Promotion Initiative
Patna, the state capital of Bihar, is situated on the southern bank of Ganga River. The city is surrounded by two other rivers on two other sides: Sone River and Pun-Pun River. Patna is the second largest city in eastern India after Kolkata. For the preparation of the SFD, the territory of Patna Municipal Corporation (PMC) is selected. The total population of the city is 1.68 […]
Kapur, D., Ramisetty, M., Barot, N. (2016) Formative Research to Develop Appropriate Participatory Approaches towards Water, Sanitation, and Hygiene in Rural Areas
Most sanitation promotion approaches are only partially successful in providing short term increases in sanitation coverage and usage. BCC messages designed as marketing interventions often fail to address deeper underlying causes of resistance behind people’s reluctance to adopt improved and safe sanitation and hygiene (or even physical barriers like water availability). This study was an intensive qualitative research, undertaken with the objective of understanding perceptions, barriers, and motivators […]
Tilmans, S., Russel, K., Sklar, R., Page, L., Kramer, S., Davis, J. (2015) Container-based sanitation assessing costs and effectiveness of excreta management in Cap Haitien, Haiti
Container-based sanitation (CBS) – in which wastes are captured in sealable containers that are then transported to treatment facilities – is an alternative sanitation option in urban areas where on-site sanitation and sewerage are infeasible. This paper presents the results of a pilot household CBS service in Cap Haitien, Haiti. We quantify the excreta generated weekly in a dense urban slum, the proportion safely removed […]
Reade, A. (2016) What Potential is there for Container Based Sanitation and the Social Enterprise in Urban Emergencies?
Traditional alternatives have included: lined pit latrines, raised latrines and urine diverting dry toilets (UDDTs). These alternatives might be suitable in addressing the unfavourable ground conditions, but are not necessarily able to address the constraints encountered in the urban environment. For this reason agencies have started to take a closer look at some of the newer container based sanitation (CBS) approaches being developed by social […]